 Read article 'Strongly unbalanced photon pairs'
Read article 'Strongly unbalanced photon pairs'
Strongly unbalanced photon pairs
By measuring the transverse momentum of photon pairs, and related observables, the strong interaction may be indirectly probed.
Thank you for registering
If you'd like to change your details at any time, please visit My account
 Read article 'Strongly unbalanced photon pairs'
Read article 'Strongly unbalanced photon pairs'
By measuring the transverse momentum of photon pairs, and related observables, the strong interaction may be indirectly probed.
 Read article 'COMPASS points to triangle singularity'
Read article 'COMPASS points to triangle singularity'
The collaboration last week reported the first direct evidence for the long-sought interplay between hadron decays, downplaying the chances that the a1(1420) is a new exotic hadron.
 Read article 'Loop Summit convenes in Como'
Read article 'Loop Summit convenes in Como'
The workshop explored new perturbative results and methods in quantum field theory, collider physics and gravity.
 Read article 'New tetraquark a whisker away from stability'
Read article 'New tetraquark a whisker away from stability'
The new state, announced today at EPS-HEP, had been held up since the 1980s as a prime candidate to be the first exotic hadronic state to be stable against strong decays.
 Read article 'Charm breaks fragmentation universality'
Read article 'Charm breaks fragmentation universality'
Charm fragmentation fractions presented today at EPS-HEP by the ALICE collaboration are the first such measurements at the LHC.
 Read article 'Experiment and theory trade blows at SQM 2021'
Read article 'Experiment and theory trade blows at SQM 2021'
The conference attracted over 300 participants to discuss the role of strange and heavy-flavour quarks in heavy-ion collisions and astrophysical phenomena.
 Read article 'LHCP sees a host of new results'
Read article 'LHCP sees a host of new results'
Over 1000 physicists took part in the ninth Large Hadron Collider Physics conference.
 Read article 'New charmed-baryon lifetime hierarchy cast in stone'
Read article 'New charmed-baryon lifetime hierarchy cast in stone'
A recent measurement by the LHCb collaboration has confirmed the measured lifetime of the doubly strange Ωc0.
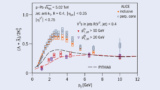 Read article 'Hadron formation differs outside of jets'
Read article 'Hadron formation differs outside of jets'
The ALICE collaboration has compared the production of strange neutral baryons and mesons inside and outside of charged-particle jets.
 Read article 'Light neutral mesons probed to high pT'
Read article 'Light neutral mesons probed to high pT'
The measurements constrain predictions from perturbative quantum chromodynamics.