 Read article 'ATLAS puts last piece in puzzle…'
Read article 'ATLAS puts last piece in puzzle…'
ATLAS puts last piece in puzzle…
The ATLAS collaboration celebrated lowering the final large piece of the detector into the underground cavern on 29 February.
Thank you for registering
If you'd like to change your details at any time, please visit My account
 Read article 'ATLAS puts last piece in puzzle…'
Read article 'ATLAS puts last piece in puzzle…'
The ATLAS collaboration celebrated lowering the final large piece of the detector into the underground cavern on 29 February.
 Read article 'ALICE and CMS line up the final big pieces underground'
Read article 'ALICE and CMS line up the final big pieces underground'
With the completion of two major installation projects, nearly all the infrastructure for the ALICE experiment is now in place in the cavern at Point 2 on the LHC ring, near St. Genis-Pouilly in Fra...
 Read article 'Positrons prefer one side of the galaxy'
Read article 'Positrons prefer one side of the galaxy'
A new study of the gamma-ray emission of positron annihilation in the Milky Way reveals an asymmetric distribution in the galactic disc. The only sources known to have a similar asymmetry are low-mass...
 Read article 'Construction of IceCube project at the South Pole reaches the halfway point'
Read article 'Construction of IceCube project at the South Pole reaches the halfway point'
The teams installing the IceCube experiment at the South Pole have completed a highly successful austral summer season, during which they installed 18 detector strings – 4 more than in the baselin...
 Read article 'Particle physics in the UK is facing a severe funding crisis'
Read article 'Particle physics in the UK is facing a severe funding crisis'
The UK increased an additional £1200 m in the budget for science but this leads to a deficit of £80 in particle physics.
 Read article 'Superstrings reveal the interior structure of a black hole'
Read article 'Superstrings reveal the interior structure of a black hole'
A research group at KEK has succeeded in calculating the state inside a black hole using computer simulations based on superstring theory.
 Read article 'The team at SPIN@COSY looks inside a spin resonance'
Read article 'The team at SPIN@COSY looks inside a spin resonance'
The SPIN@COSY polarized-beam team has found striking new results while studying the spin-manipulation of polarized deuterons at the Cooler Synchrotron (COSY) at the Forschungszentrum in Jülich.
 Read article 'Hot plasma fills the Orion nebula'
Read article 'Hot plasma fills the Orion nebula'
Observations with the XMM-Newton satellite have revealed soft X-ray emission from an extended region in the Orion nebula. The most massive stars in the heart of the nebula are probably at the origin o...
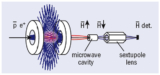 Read article 'ASACUSA moves towards new antihydrogen experiments'
Read article 'ASACUSA moves towards new antihydrogen experiments'
Recently, the Japanese–European group made the first steps towards producing a low-velocity antihydrogen beam.
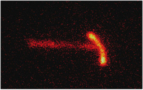 Read article 'Camera captures image of two-proton decay'
Read article 'Camera captures image of two-proton decay'
In work that harks back to the early days of nuclear physics, an international team of researchers at Michigan State University's National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory (NSCL) has used a novel ...