 Read article 'Julius Wess Award 2018'
Read article 'Julius Wess Award 2018'
Julius Wess Award 2018
Sally Dawson of Brookhaven National Laboratory has been recognised for her outstanding contributions to the theoretical description of processes at hadron colliders.
Thank you for registering
If you'd like to change your details at any time, please visit My account
 Read article 'Julius Wess Award 2018'
Read article 'Julius Wess Award 2018'
Sally Dawson of Brookhaven National Laboratory has been recognised for her outstanding contributions to the theoretical description of processes at hadron colliders.
 Read article 'Winners of 2019 Beamline for Schools competition'
Read article 'Winners of 2019 Beamline for Schools competition'
A Dutch team will compare electron and positron showers, while a US team will study the properties of scintillators.
 Read article 'Bottomonium elliptic-flow no-show'
Read article 'Bottomonium elliptic-flow no-show'
Bottomonia are the first hadrons that do not seem to "flow" in heavy-ion collisions at the LHC.
 Read article 'Dipole marks path to future collider'
Read article 'Dipole marks path to future collider'
Researchers in the US have demonstrated an advanced accelerator dipole magnet with a field of 14.1 T.
 Read article 'Cloud services take off in the US and Europe'
Read article 'Cloud services take off in the US and Europe'
Fermilab has announced the launch of HEPCloud, a step towards a new computing paradigm to deal with the vast quantities of data pouring in from existing and future facilities.
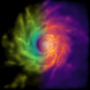 Read article 'Galaxies thrive on new physics'
Read article 'Galaxies thrive on new physics'
Theorists at Durham University simulated the universe using hydrodynamical simulations in which a scalar field enhances gravitational forces in low-density regions.
 Read article 'Supergravity pioneers share $3m Breakthrough Prize'
Read article 'Supergravity pioneers share $3m Breakthrough Prize'
Marriage of supersymmetry and general relativity continues to impact theoretical physics.
 Read article 'Austrian synchrotron debuts carbon-ion cancer treatment'
Read article 'Austrian synchrotron debuts carbon-ion cancer treatment'
MedAustron becomes one of six centres worldwide to treat tumours with carbon ions.
 Read article 'Niobium-tin cavities for smaller accelerators'
Read article 'Niobium-tin cavities for smaller accelerators'
High-frequency superconducting radio-frequency cavities made from niobium–tin alloy are more efficient than conventional niobium designs.
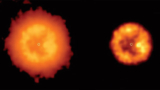 Read article 'Clocking the merger of two white dwarfs'
Read article 'Clocking the merger of two white dwarfs'
As two white dwarfs orbited one another they slowly lost momentum through the emission of gravitational waves.