Read article 'Lead collisions in the LHC top the bill in Cagliari'
Read article 'Lead collisions in the LHC top the bill in Cagliari'
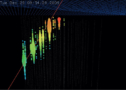
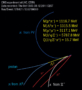
Lead collisions in the LHC top the bill in Cagliari
Hard Probes 2012 – the 5th International Conference on Hard and Electromagnetic Probes of Nuclear Collisions – took place in Cagliari on 27 May – 1 June.