 Read article '…and investigates suppression of ψ(2S)'
Read article '…and investigates suppression of ψ(2S)'
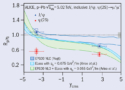
…and investigates suppression of ψ(2S)
Charmonia, bound states of charm and anti-charm quarks, are probes for the formation of hot quark–gluon plasma (QGP) in heavy-ion collisions.
Thank you for registering
If you'd like to change your details at any time, please visit My account
 Read article '…and investigates suppression of ψ(2S)'
Read article '…and investigates suppression of ψ(2S)'
Charmonia, bound states of charm and anti-charm quarks, are probes for the formation of hot quark–gluon plasma (QGP) in heavy-ion collisions.
 Read article 'Heavy-ion collisions: where size matters'
Read article 'Heavy-ion collisions: where size matters'
Results from ALICE provide insight into the size of the final state at “freeze-out” – and a window on collective behaviour.
 Read article 'Cosmic particles meet the LHC at ISVHECRI'
Read article 'Cosmic particles meet the LHC at ISVHECRI'
More than 120 physicists from across the world met at CERN to discuss questions related to hadron production in cosmic-ray interactions and at accelerator experiments.
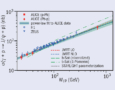 Read article 'Producing charm with light'
Read article 'Producing charm with light'
The electric charge of lead ions, when accelerated to ultra-relativistic velocities, is the source of an intense flux of high-energy quasi-real photons.
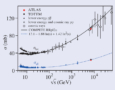 Read article 'ALFA in ATLAS measures pp cross-section with high precision'
Read article 'ALFA in ATLAS measures pp cross-section with high precision'
Data from a special run of the LHC using dedicated beam optics at 7 TeV have been analysed to measure the total cross-section of proton–proton collisions in ATLAS.
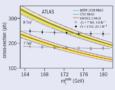 Read article 'Precise measurements of top-quark production'
Read article 'Precise measurements of top-quark production'
The top quark is the heaviest-known fundamental particle, whose mass of about 173 GeV is much larger than that of the other quarks, and comparable to those of the W, Z and Higgs bosons.
 Read article 'COSY confirms existence of six-quark states'
Read article 'COSY confirms existence of six-quark states'
Experiments at the Jülich Cooler Synchrotron (COSY) have found compelling evidence for a new state in the two-baryon system, with a mass of 2380 MeV and width of 80 MeV
 Read article 'ALICE and the flowing particle zoo'
Read article 'ALICE and the flowing particle zoo'
Relativistic heavy-ion collisions produce large numbers of particles that do not move individually, but rather as an organized group, with a collective motion known as flow. Flow studies at Brookhaven...
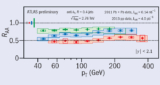 Read article 'New results from ATLAS at Quark Matter 2014'
Read article 'New results from ATLAS at Quark Matter 2014'
At the Quark Matter 2014 conference, held in Darmstadt on 19–25 May, ATLAS presented a variety of new results based on lead–lead (PbPb) and proton–lead (pPb) data collected during Run 1 of the...
 Read article 'Quark Matter 2014: news from ALICE'
Read article 'Quark Matter 2014: news from ALICE'
The new results shown by the ALICE collaboration at the Quark Matter 2014 conference in Darmstadt focus principally on the most recent collisions at the LHC – those of protons and lead nuclei (p...