Read article 'LHC and RHIC heavy ions dovetail in Wuhan'
Read article 'LHC and RHIC heavy ions dovetail in Wuhan'
LHC and RHIC heavy ions dovetail in Wuhan
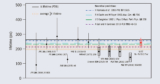
Quark Matter 2019 heard about new probes of the quark-gluon plasma, including first observations of the exotic hadron X(3872) and top-antitop production.