 Read article 'Fixed-target physics in collider mode at LHCb'
Read article 'Fixed-target physics in collider mode at LHCb'
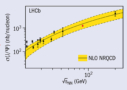
Fixed-target physics in collider mode at LHCb
The LHCb fixed-target system, known as SMOG, injects a small amount of noble gas inside the LHC beam pipe.
Thank you for registering
If you'd like to change your details at any time, please visit My account
 Read article 'Fixed-target physics in collider mode at LHCb'
Read article 'Fixed-target physics in collider mode at LHCb'
The LHCb fixed-target system, known as SMOG, injects a small amount of noble gas inside the LHC beam pipe.
 Read article 'Observation of Higgs-boson decay to bottom quarks'
Read article 'Observation of Higgs-boson decay to bottom quarks'
Processes that include the Higgs boson’s favoured decay mode to b quarks (with about 58% probability) have until now remained elusive.
 Read article 'Solving the mystery of a historic stellar blast'
Read article 'Solving the mystery of a historic stellar blast'
Some 180 years ago, a relatively normal star called Eta Carinae suddenly brightened to become the second brightest star in the sky, before almost disappearing at the end of the 19th century.
 Read article 'Francis Farley 1920–2018'
Read article 'Francis Farley 1920–2018'
He received many honours, including election to a fellow of the Royal Society and the Hughes Medal for his work at CERN on g-2.
 Read article 'IceCube neutrino points to origin of cosmic rays'
Read article 'IceCube neutrino points to origin of cosmic rays'
On 22 September 2017, IceCube registered a 300 TeV neutrino of astrophysical origin, triggering worldwide follow-up observations.
 Read article 'CMS looks into the dark'
Read article 'CMS looks into the dark'
If dark-QCD mediators were produced in pairs in the CMS detector, their signature would be striking.
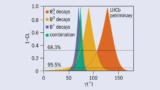 Read article 'LHCb tests consistency of unitarity triangle'
Read article 'LHCb tests consistency of unitarity triangle'
The unitarity triangle exists in the complex plane and its area is a measure of the amount of CP violation in the Standard Model.
 Read article 'Probing quark–gluon plasma with charmed mesons'
Read article 'Probing quark–gluon plasma with charmed mesons'
The ALICE collaboration has released a new measurement of the production of D mesons.
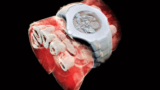 Read article 'First human 3D X-ray in colour'
Read article 'First human 3D X-ray in colour'
New-Zealand company MARS Bioimaging Ltd has used technology developed at CERN to perform the first colour 3D X-ray of a human body, offering more accurate medical diagnoses.
 Read article 'Closing in on the muon’s magnetic moment'
Read article 'Closing in on the muon’s magnetic moment'
Experiment E989 is a reincarnation of the muon g-2 experiment at BNL, which found the muon’s anomalous magnetic moment to be 3.5 sigma above the Standard Model prediction.